The Keto vs. LCHF Debate: Which One Is Better?

You’ve probably heard a lot about low-carb diets. It’s a popular conversation in the health world, certainly if you’re looking to shed a few pounds.
There are many out there, but two stand out.
The LCHF (low carb, high fat) and ketogenic diets are well-known diets, most commonly used for weight loss.
The core principle of each is to restrict carbohydrate intake, swapping it for high-fat foods.
At a glance, the two appear pretty much the same concept. But on review, there are slight differences between them.
If you’re looking to switch to an effective eating plan to lose weight, you might be torn between an LCHF and keto diet. There’s a debate over the better diet, but what makes one better than the other?
In this article, we identify the similarities and the differences to help you decide which one is more fitting for you and your lifestyle.
Is LCHF the Same as Keto?
When you summarize the two, low carb and keto are characterized as carb-restrictive diets. With that information, one might assume they are the same thing.
In reality, there are distinguishable differences between LCHF and keto diets.
Both claim to bring significant health benefits such as reducing high blood pressure, balancing blood sugars, and promoting weight loss through more mindful eating.
Keep reading as we go into more detail.
What does LCHF stand for?
LCHF stands for “low carb, high fat” and is a modification of a well know keto diet. LCHF is less restrictive than keto but has similar benefits.
What is LCHF Diet
As mentioned above, LCHF stands for low carbohydrate high fat. The theory behind LCHF is, as the name suggests, to cut back your carb intake and increase your fat intake.
The low carb approach requires you to eat only small amounts of carbohydrate-based foods. It means cutting down on foods like bread, pasta, and sugary drinks.
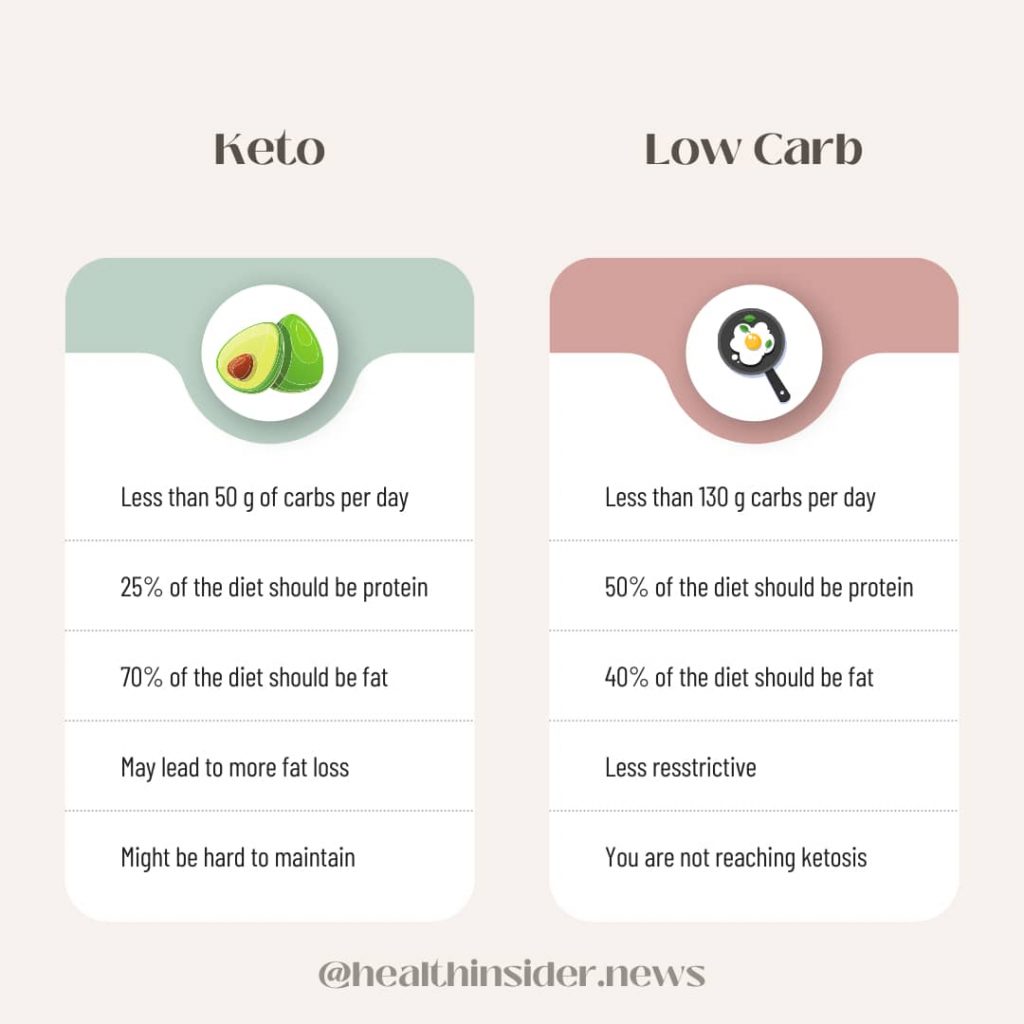
With a generous low-carb diet, you can expect to eat around 100-150 grams of carbs per day while when on keto you have to consume no more than 50 grams of carbs.

Advertisement
That said, the low-carb diet doesn’t strictly calculate what you eat, unlike keto diets.
You wind up eating fewer calories and avoiding highly processed foods by restricting carbs. For this reason, a reduction in body fat is a typical result of following the diet, which is why many turn to it for weight loss.
To ensure you get enough calories, you need to consume more healthy fats and increase your protein intake.
The low-carb diet is considered more of a lifestyle change than a restrictive diet. It provides recommendations for daily carb intake, but there are no strict numbers that you must adhere to.
There are a variety of low-carb diets in existence, including the Atkins diet and the low-carb Mediterranean diet. You should explore the different eating plans if you’re interested in giving low carb a go.
Low Carb Pros and Cons
When reviewing which low-carb diet to try, weighing out the advantages and disadvantages is a good starting point. It’s vital to understand the risks or adverse side effects involved before you commit your time to it.
Keto Diet
The keto diet or ketogenic diet is a restrictive diet that drastically reduces the consumption of carbs. You eat more fat, and less protein.
The goal is to reach nutritional ketosis, a metabolic state where ketones are produced, driving your body to burn fat for fuel.
In starving the body of carbohydrates, the glucose that your body usually uses as an energy source depletes. As the body searches for alternative fuel, it turns to stored body fat.
Therefore in ketosis, fat burns more quickly.

To achieve nutritional ketosis, you can only consume a minimal number of carbs. A typical keto diet consists of only 50 grams of carbs per day, with some people consuming as little as 20 grams per day.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans suggest that carbs make up 45-60 percent of total calories. With a 2000 calorie diet, the math works out at around 225-325 grams per day. As you can see, it’s a considerable reduction.
Eat meats such as grass-fed beef, fatty fish, full-fat dairy, and low-carb vegetables for a healthy keto lifestyle. Meanwhile, avoid grains, starches, low-fat products, and unhealthy fats.
Most keto dieters count net carbs to keep track of their intake. Net carbs are the total carb count within foods, minus the fiber.
Keto Diet Pros and Cons
We’ve looked at the pros and cons of the low-carb diet. Now let’s see the keto diet benefits and potential risks below.
Difference Between LCHF and Keto: Which One Is Better?
There is no easy answer to which is the better diet between low carb and keto.
A diet plan is personal, particularly for a weight loss journey. There is no right or wrong answer, but it’s crucial that you carefully review the health benefits as well as the potentially harmful effects of each diet.
From there, you can determine which one is better suited to your lifestyle, body type, and current health situation.
The key factor is how many carbs you are willing to eliminate. You can either opt for the strict ketogenic diet or the low-carb diet that allows you slightly more carbs.
And it’s not just carbs to think about either. The low-carb, high-fat diet includes plenty of protein, while you can only eat protein in small to moderate quantities with the keto diet.
For most healthy people, it’s safe to try either diet. But if you’re looking for a more sustainable lifestyle change, low carb diets are considered more sustainable. It’s less restrictive, more lenient, and still allows you to get your calories from most food groups.
Many people fail on the keto diet as it is highly demanding. It can be difficult to keep up in the long term with rigid carb calculations.
Before trying very low-carb diets, it’s essential to consult your doctor to ensure your suitability.
A Word From our RD
Ketogenic diets and low-carb diets are similar, but they have fundamental differences.
Both are a popular choice for losing weight, while many people use them for their proclaimed medical benefits.
Low carb consumption may induce weight loss, reduce blood pressure, improve blood sugar control, improve glycemic control, and improve insulin resistance.
In short, a low-carb diet consists of fewer carbs, high protein, and healthy fats for your daily calorie intake.
Keto diets consist of very few carbs, low to moderate protein, and a high intake of fat.
Whatever your reasons for starting a diet low in carbohydrates, you should choose the most appropriate eating plan for you and incorporate it as part of a healthy regime.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve debated LCHF vs. keto. While there is no clear answer, it’s clear that there are positive and negative aspects of each.
Whichever you decide to try, you should always aim to eat healthy foods, regardless of your permission for increasing fat intake. Choose good dietary fat, non-starchy vegetables, and limit sugary and refined foods to maintain overall good health.





Comments (0)