The Connection Between Intermittent Fasting and Diarrhea: Causes and Solutions
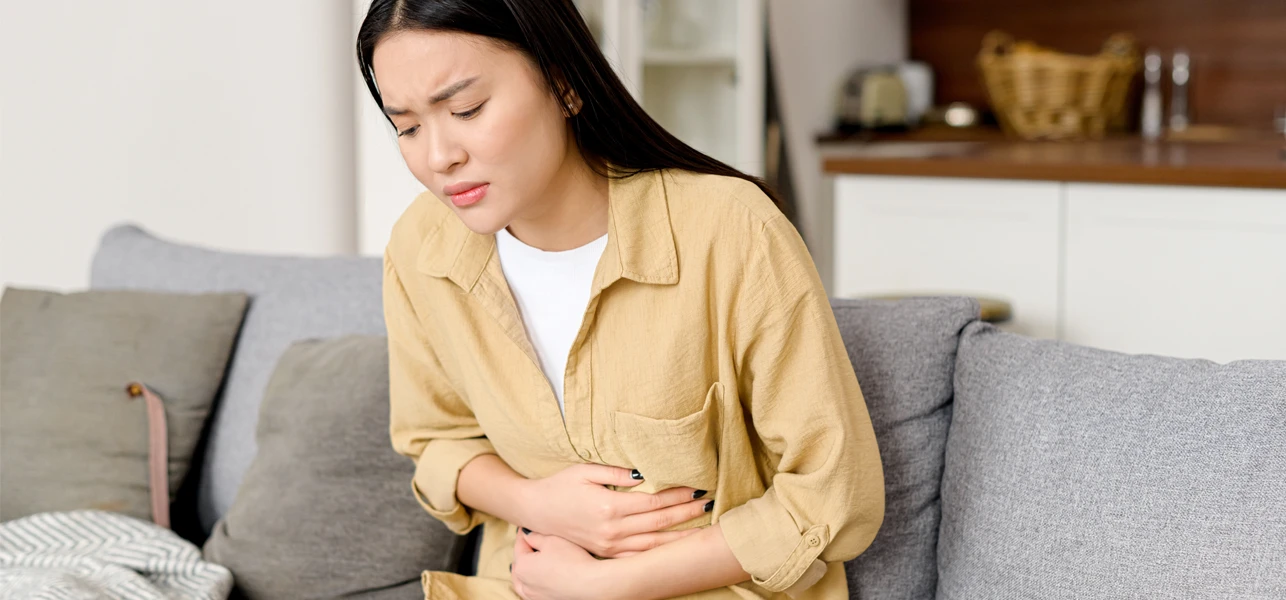

Diarrhea is the condition that describes the persistent emptying of the bowels. The stool is loose and watery and may be accompanied by abdominal cramps, bloating, and nausea.
Many internal and external factors can contribute to bowel issues. It could be a bacterial infection, virus, food poisoning, intolerance, or intestinal disease. Changing your diet can also trigger problems with your gut health, and that includes starting a new fasting routine.
This article looks at the link between intermittent fasting and frequent, loose bowel movements.
Intermittent Fasting-Related Diarrhea: Is It Common?
Diarrhea is one of the less common intermittent fasting side effects, but it does happen. However, it is usually a result of other things and not the fasting itself. There are a handful of causes for diarrhea during fasting periods, like consuming caffeinated drinks and zero-calorie sweeteners.
You are more likely to experience diarrhea when you break your fast. That’s because your gut is sensitive at this time, especially after multiple hours without food. The digestive system slows, and you may have trouble digesting certain foods when you begin eating again.
Sometimes, you might experience the opposite and get hit with constipation. Constipation is more likely to occur when practicing intermittent fasting due to poor hydration and fiber intake.
How to Prevent Intermittent Fasting Diarrhea: 4 Tips to Try Today
You can prevent diarrhea with some simple strategies. Primarily, it’s about being mindful of what you put into your body. Try these 4 tips to keep your bowel movements healthy throughout the fasting period.
#1 Stay hydrated
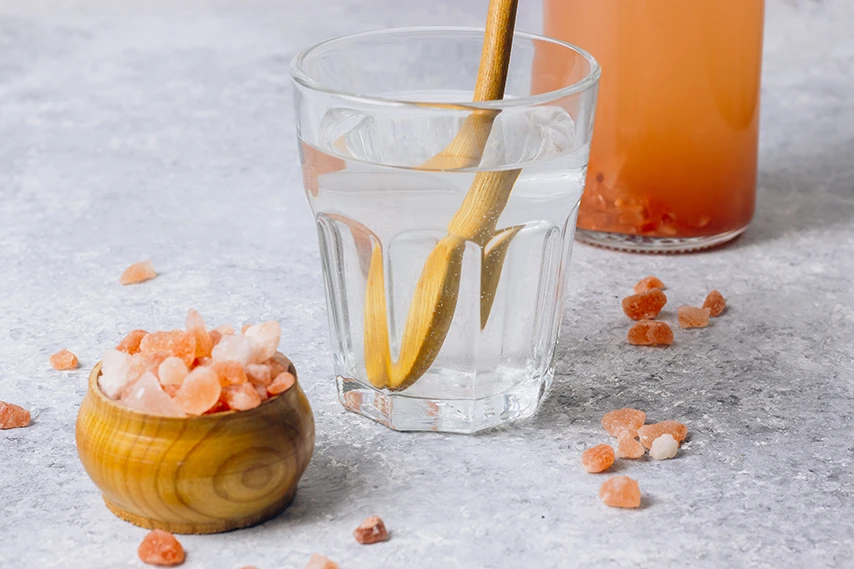
Hydration is essential for keeping a happy gut. It helps improve digestion, regulates bowel habits, and prevents constipation. One of the key strategies for treating diarrhea is to drink plenty of water. It may help treat diarrhea symptoms faster and prevent dehydration.
Diarrhea causes significant water loss, which can lead to severe dehydration – a life-threatening condition if left untreated. Drink lots of fluids throughout the day, especially after experiencing diarrhea during fasting.
Water is best, but you can also try oral rehydration solutions to speed up hydration. Bone broth is another hydrating beverage full of goodness, and it’s gentle on an empty stomach. Herbal teas also make an excellent choice because they are high in antioxidants.
#2 Take electrolyte supplements
Electrolytes are important minerals your body needs to survive. A healthy diet is usually enough to maintain an electrolyte balance, but keep in mind that you’re taking in fewer nutrients when fasting. An electrolyte imbalance can result in diarrhea, constipation, and cramps, among other symptoms.
Taking electrolytes while fasting will help ensure balance. It will also prevent you from becoming dehydrated due to diarrhea. However, too many electrolytes can also trigger diarrhea. For example, increasing sodium levels may cause dizziness and diarrhea.
Do your research and discover the best fasting supplements for your unique needs.

Advertisement
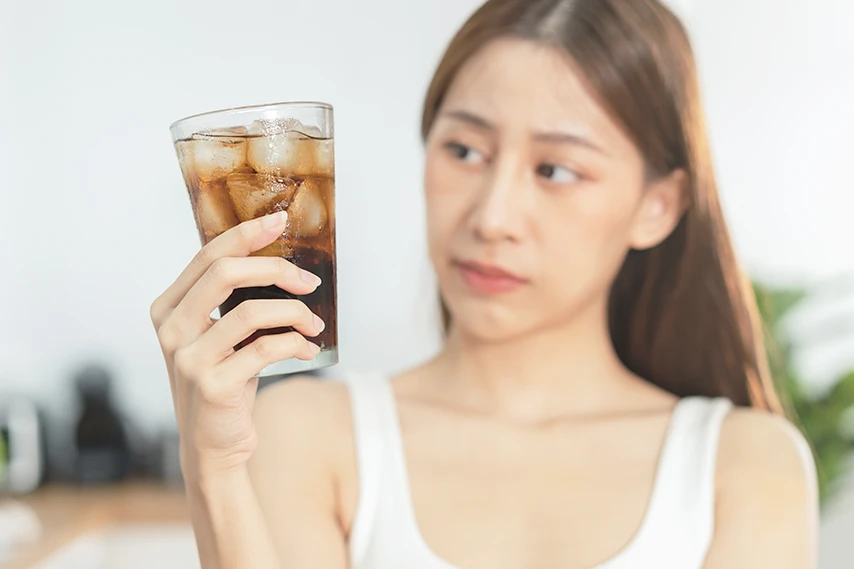
#3 Avoid caffeinated beverages
You can drink coffee, green tea, and other caffeinated drinks without breaking your fast. It contains zero calories and can help you lose weight by curbing your appetite and boosting energy levels. However, caffeine is the number one culprit for diarrhea during fasting.
It’s a natural stimulant that increases gut motility, causing diarrhea. It can irritate the digestive tract and may cause an upset stomach in people with low tolerance. It’s recommended that you eliminate caffeine from your diet if you have diarrhea and see if it helps.
#4 Don’t use zero-calorie sweeteners
Zero-calorie sweeteners are notorious for causing diarrhea because large amounts can produce laxative effects. Studies show that a diet containing zero-calorie sweeteners can increase diarrhea, postprandial discomfort, and constipation.
Diet soda is an example of a zero-calorie sweetened beverage. It won’t break your fast, but it will provide artificial sweeteners that aren’t good for your health. They usually contain popular additives like cyclamates, aspartame, acesulfame-K, sucralose, or saccharin.
Cutting these ingredients from your meal plan might clear up those watery stools.

Why Does Intermittent Fasting Cause Diarrhea?
Intermittent fasting can cause diarrhea temporarily because your digestive system is trying to adapt to a new way of functioning. Changes occur when you stop eating, and this disturbance to the gastrointestinal tract can alter your bowel habits. Your body just needs time to transition.
You can avoid diarrhea by taking precautions to limit problems. For example, consuming small meals with easily-digestible ingredients after you break your fast will help your system resume gently. In time, intermittent fasting can work wonders for your gut health.
Other Potential Side Effects of Fasting
You can expect some side effects with intermittent fasting, especially as a newbie. Preparing for these symptoms can make you better equipped for the diet so that you continue to enjoy the health benefits.
Diarrhea is one of the less common side effects, but you might experience the following symptoms:
- Nausea
- Hunger
- Food cravings
- Headaches
- Lightheadedness
- Low energy
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Sleep problems
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
More severe side effects are dehydration and malnutrition. For this reason, it is absolutely critical that you follow the dietary plan correctly and identify the best fasting method for you.
FAQs
An intermittent fast can help clean and restore your gut. Research suggests the practice has several gut health benefits, including altering and diversifying the human gut microbiome.
Mild and temporary diarrhea is not usually a warning sign to stop fasting. However, persistent and chronic bouts of diarrhea during fasting can indicate a bigger problem. In that case, you should stop fasting and consult with your doctor immediately for advice.
Consuming food only once a day can indeed cause diarrhea. Your digestive processes slow down when you don’t eat, and the system can struggle to cope with the sudden introduction of your first meal. This can limit nutrient absorption if diarrhea persists.
Those already experiencing diarrhea may want to skip fasting, as it might make symptoms worse. On the other hand, fasting periods may provide relief for IBS symptoms, including diarrhea, by maintaining a healthy gut microbiota. It’s best to discuss this with your doctor.
A Word From MD
Intermittent fasting can benefit your overall health. Many people utilize the practice to lose weight. Others use it for health reasons, like stabilizing insulin levels, reducing insulin resistance, regulating blood sugar levels, and decreasing the risk of heart disease.
Digestive issues are common symptoms of intermittent fasting. Diarrhea is less likely but can occur after long periods without food, eating high-fat foods, or drinking lots of caffeine. You can consume lots of water, take supplements, and avoid caffeine to help alleviate symptoms.
Other tips include eating a healthy diet and breaking your fast with a small and healthy meal that helps bring your system back to its usual function. If stress is causing your digestive woes, physical activity can help relieve tension and prevent stress-related ailments.
Seek professional medical advice before implementing a fasting regimen. Furthermore, you should seek medical attention if you experience frequent diarrhea, blood in the stool, extreme weakness, severe abdominal or rectal pain, or a high fever.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, intermittent fasting can cause some people to experience temporary diarrhea. Watery stools are an inconvenience, but they don’t have to be. A few simple tips can mitigate fasting diarrhea and make it easier to reach your goals.
If you continue to struggle with diarrhea while fasting, it’s time to rethink your method. Persistent diarrhea can be life-threatening if it leads to dehydration. Contact your doctor immediately if it persists or if you experience other symptoms, such as dizziness or bloody stools.






Comments (0)